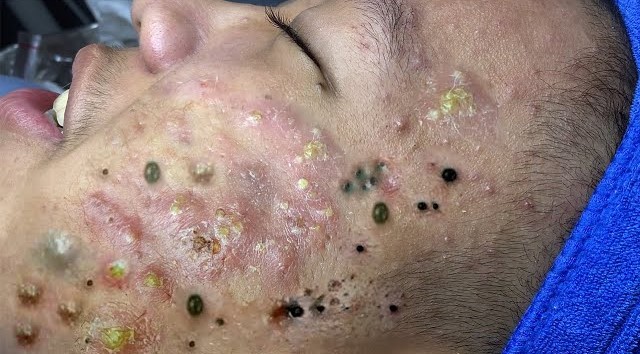
Pre-treatment for facial care is essential to ensure that your skin is properly prepared for any facial treatment, whether it’s a simple facial, chemical peel, microdermabrasion, or laser treatment. Proper pre-treatment can enhance results, prevent irritation, and promote healing.
General Pre-Treatment Steps for Facial Care
Cleansing – Wash your face with a gentle cleanser to remove dirt, oil, and makeup.
Exfoliation (If Recommended) – Light exfoliation a few days before can help remove dead skin cells, but avoid harsh scrubs before strong treatments.
Hydration – Keep your skin well-moisturized before any facial treatment to maintain a healthy barrier.
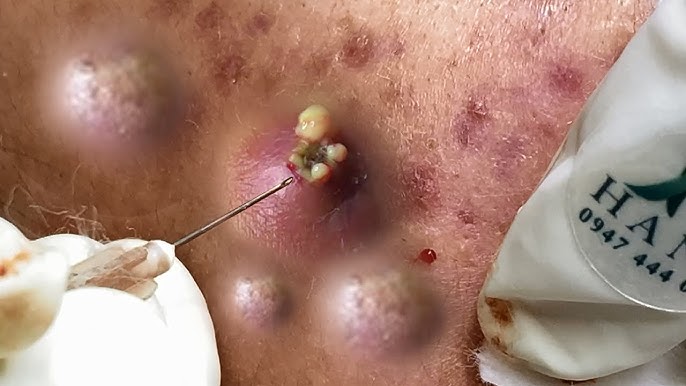
Avoid Harsh Ingredients – Stop using retinoids, AHAs, BHAs, or strong acids 3-5 days before treatments like chemical peels or laser treatments.
Sun Protection – Avoid excessive sun exposure and wear SPF 30+ daily to prevent sensitivity.
Stay Hydrated & Eat Well – Drinking plenty of water and maintaining a balanced diet can improve skin resilience.
Stop Waxing or Shaving – If you’re getting a treatment like microdermabrasion or a chemical peel, avoid hair removal for at least 24-48 hours before.
Consult with Your Esthetician or Dermatologist – They may have specific recommendations based on your skin type and the treatment you’re receiving.
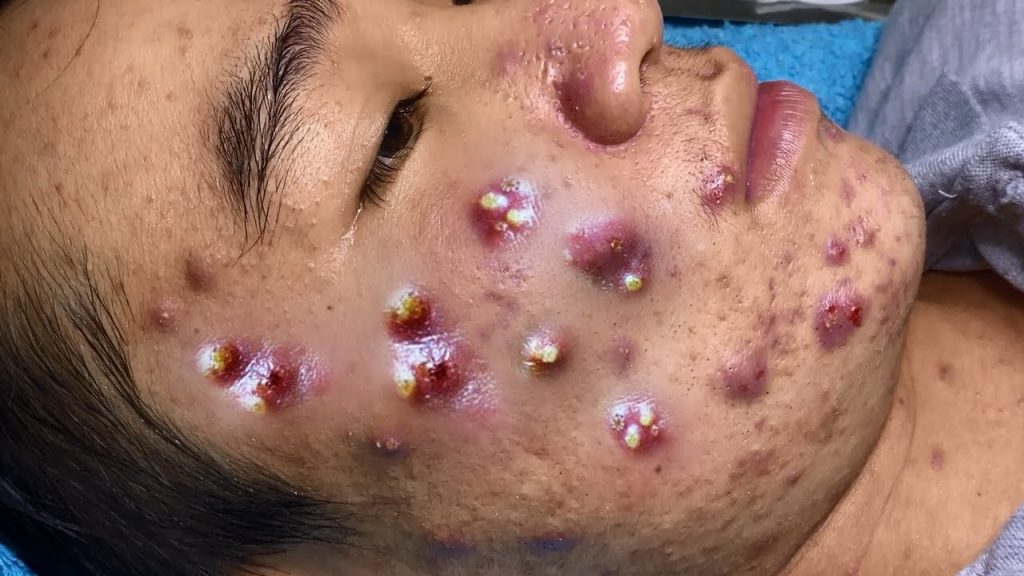
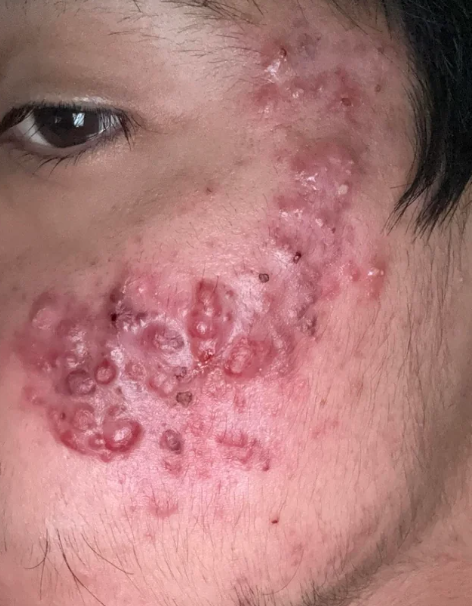
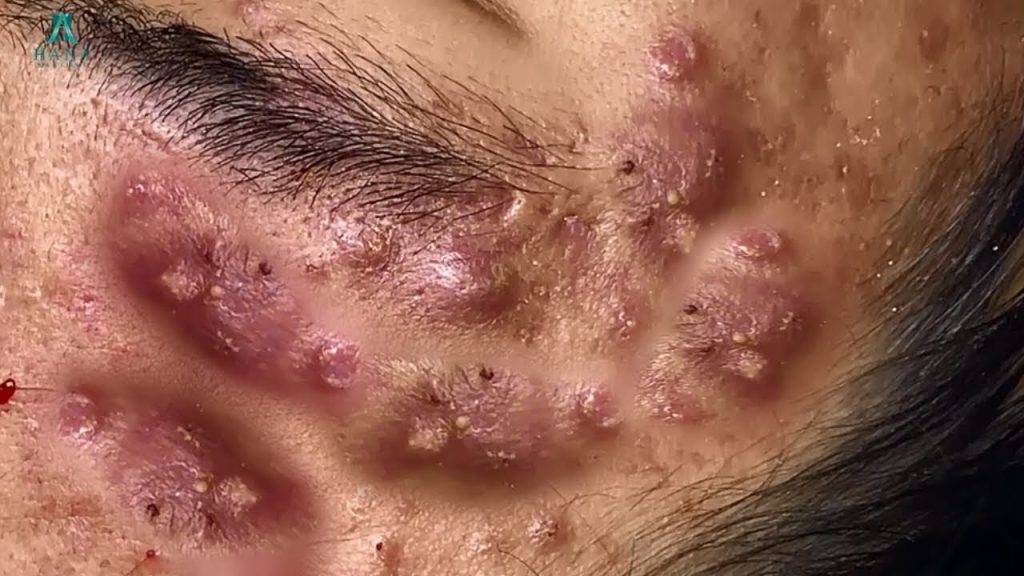
Acne is caused by a variety of factors, and it’s typically the result of a combination of these. Here are the most common causes:
1. Excess Oil Production (Sebum)
Your skin naturally produces oil to keep it moisturized, but when excess oil is produced, it can clog pores, leading to acne. This often occurs during puberty, hormonal changes, or as a result of stress.
2. Clogged Pores
Dead skin cells can build up and mix with oil, clogging hair follicles or pores. When these clogged pores become infected with bacteria, pimples and blackheads can form.
3. Bacteria
Propionibacterium acnes is a bacterium that lives on your skin. When hair follicles become clogged with excess oil and dead skin cells, the bacteria can multiply, causing inflammation, which leads to acne.
4. Hormonal Changes
Hormonal fluctuations, especially during puberty, menstruation, pregnancy, or conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), can increase sebum production. This is one of the main reasons teenagers often experience acne.
5. Diet
Some studies suggest that high-glycemic foods (like sugary and processed foods) and dairy products may worsen acne. However, the connection between diet and acne can vary for each person.
6. Stress
Stress triggers the release of hormones like cortisol, which can increase oil production and lead to acne breakouts. Emotional or physical stress can worsen existing acne.
7. Medications
Certain medications, including steroids, birth control pills (in some cases), or other drugs that affect hormone levels, can lead to acne as a side effect.
8. Genetics
If your parents had acne, you’re more likely to develop it as well. Genetic factors influence how much oil your skin produces, your skin’s healing abilities, and how sensitive your pores are.
9. Environmental Factors
Pollution, exposure to oils, and humidity can also clog pores and contribute to acne. For instance, if you live in a highly polluted area or wear heavy makeup, your skin may be more prone to breakouts.
10. Poor Skincare Habits
Using harsh products, over-cleansing, or touching your face too often can irritate the skin and lead to acne. Additionally, using oily or comedogenic (pore-clogging) products can worsen acne.
11. Sleeping with Makeup
Not removing makeup at night can lead to clogged pores and the buildup of oils, which may trigger acne.
If you’re experiencing acne, it can help to consult with a dermatologist to determine the specific causes in your case and develop an appropriate treatment plan.
Here are a few more factors that can contribute to acne development:
12. Hormonal Imbalances
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): Women with PCOS often experience acne due to hormonal imbalances. Elevated levels of androgens (male hormones) can increase oil production in the skin.
Birth Control Pills: While some forms of birth control can help reduce acne, others, particularly those that affect estrogen and progesterone levels, can exacerbate it.
13. Overuse of Skincare Products
While skincare is important, using too many products or harsh products in an attempt to control acne can irritate the skin and make things worse. Products containing strong exfoliants or alcohol can strip the skin, causing it to produce even more oil.
14. Touching or Picking Your Face
Constantly touching your face, resting your chin on your hand, or picking at pimples can introduce more bacteria to the skin and cause inflammation. Picking at acne lesions can also lead to scarring.
15. Menstrual Cycle
Many women notice an increase in acne around the time of their period, due to hormonal fluctuations that stimulate oil production. These breakouts often occur along the jawline and chin.
16. Skin Sensitivity
Some people have more sensitive skin, which can react more easily to changes in the environment, products, or hormonal shifts. This can lead to a higher tendency to break out.
17. Friction or Pressure on the Skin (Acne Mechanica)
Any friction on the skin, such as from wearing tight clothing, helmets, or backpacks, can irritate the skin and lead to acne. This is often called “acne mechanica.” It’s common for athletes who wear headgear or for people who wear tight collars.
18. Dehydration
When the skin is not properly hydrated, it can become irritated, leading to an overproduction of oil. This excess oil can clog pores and result in acne breakouts. Drinking plenty of water can help maintain proper hydration and balance skin oils.
19. Cosmetic Products
Some makeup, lotions, or creams contain ingredients that can clog pores, known as comedogenic ingredients. It’s important to use non-comedogenic (non-pore-clogging) products if you’re prone to acne.
20. Environmental Allergens
Exposure to allergens like pollen, dust mites, or other airborne irritants can trigger skin reactions that contribute to acne. In some cases, environmental allergens may cause inflammation in the skin, leading to breakouts.
21. Gut Health
The gut-skin connection is a growing area of research. An imbalance of gut bacteria (dysbiosis) may contribute to inflammatory conditions, including acne. Certain foods that disrupt gut health, like processed foods, can exacerbate skin conditions.
22. Smoking
Smoking can reduce blood flow to the skin, making it harder for the skin to repair itself. This can result in clogged pores and an increased risk of acne breakouts. The toxins from cigarettes can also worsen inflammation in the skin.
23. Overheating or Sweating
Excessive heat or sweating, such as from intense exercise or hot environments, can irritate the skin and contribute to acne, especially if sweat is not promptly washed off. Sweat can mix with oil and clog pores, leading to breakouts.
24. Genetic Sensitivity to Certain Triggers
Some people may have a genetic predisposition to react more strongly to triggers like stress, diet, or hormonal changes. Their immune system may also be more likely to respond with inflammation in the skin, leading to acne.
25. Medications
Besides oral contraceptives, other medications like corticosteroids, certain antidepressants, and lithium have been linked to acne breakouts. The acne might occur as a side effect due to changes in hormones or the immune system.
Acne is a multifaceted condition, and what causes it for one person may differ from another. Identifying your specific triggers and consulting a dermatologist can help you manage and treat it effectively
Videos more detail :