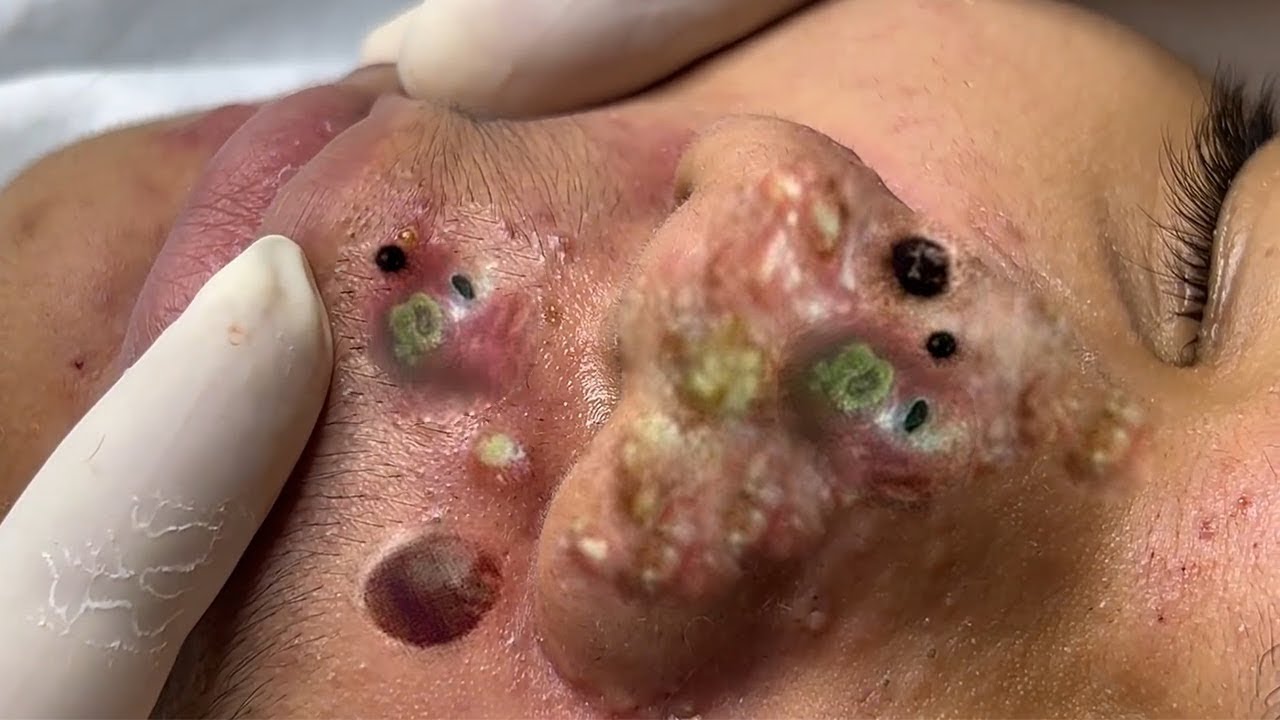
Red Spots on Your Face
Please scroll down to watch the video.👇👇
Red spots on the face can be caused by various factors, including acne, rosacea, allergies, irritation, broken capillaries, or even sunburn. Here’s a practical guide to help reduce or eliminate them, depending on the cause:
🔍 1. Identify the Cause
-
Acne or pimples – inflamed spots, often with whiteheads or blackheads.
-
Rosacea – chronic redness, often with visible blood vessels and sensitivity.
-
Allergic reaction or irritation – may be itchy, dry, or inflamed.
-
Broken capillaries – tiny red lines, usually on cheeks or nose.
-
Sunburn – red, warm, and sometimes peeling skin.
If you’re unsure, a visit to a dermatologist is best.
🧴 2. Gentle Skin Care Routine
-
Cleanser: Use a fragrance-free, gentle cleanser twice daily.
-
Moisturizer: Pick one for sensitive or redness-prone skin (look for ceramides or hyaluronic acid).
-
Sunscreen: Daily SPF 30+ helps prevent further irritation and pigmentation.
💊 3. Targeted Treatments
-
For Acne:
-
Benzoyl peroxide (anti-bacterial)
-
Salicylic acid (exfoliating)
-
Niacinamide (anti-inflammatory)
-
-
For Redness/Rosacea:
-
Azelaic acid (gentle and effective)
-
Metronidazole cream (prescription)
-
Green-tinted primers (color correction)
-
-
For Irritation:
-
Hydrocortisone cream (short-term use)
-
Avoid triggers (harsh skincare, hot water, spicy foods)
-
💆 4. Lifestyle Tips
-
Stay hydrated.
-
Avoid excessive alcohol or spicy foods (can trigger redness).
-
Manage stress — it can flare up acne and rosacea.
💡 5. When to See a Dermatologist
-
If red spots persist for more than a few weeks.
-
If they’re painful, spreading, or worsening.
-
If over-the-counter treatments don’t help.
Red spots on the face can stem from various causes, each requiring specific treatments. Here’s a comprehensive guide to help you identify and manage them effectively:
🔍 Common Causes of Facial Red Spots
1. Acne (Acne Vulgaris)
-
Appearance: Inflamed red pimples, whiteheads, or blackheads.
-
Cause: Clogged pores due to excess oil, dead skin cells, and bacteria.
-
Treatment:
-
Over-the-counter (OTC) products containing benzoyl peroxide or salicylic acid.
-
Topical retinoids to promote cell turnover.
-
For severe cases, consult a dermatologist for prescription medications.
-
2. Rosacea
-
Appearance: Persistent facial redness, visible blood vessels, and sometimes acne-like bumps.
-
Cause: Chronic inflammatory skin condition with triggers like sun exposure, spicy foods, and alcohol.
-
Treatment:
-
Topical medications such as metronidazole or azelaic acid.
-
Oral antibiotics for moderate to severe cases.
-
Laser therapy for visible blood vessels.
-
Daily use of sunscreen to prevent flare-ups.
-
3. Contact Dermatitis
-
Appearance: Red, itchy rash that may blister or peel.
-
Cause: Allergic reaction or irritation from substances like cosmetics, soaps, or plants.
-
Treatment:
-
Identify and avoid the irritant or allergen.
-
Apply topical corticosteroids to reduce inflammation.
-
Use gentle, fragrance-free skincare products.
-
4. Broken Capillaries (Telangiectasia)
-
Appearance: Small, visible red or purple blood vessels, often on the cheeks or nose.
-
Cause: Sun damage, aging, rosacea, or physical trauma to the skin.
-
Treatment:
-
Laser therapy (e.g., IPL) to reduce visibility.
-
Topical treatments with vitamin K to strengthen vessel walls.
-
Avoid excessive sun exposure and use sunscreen.
-
5. Sunburn
-
Appearance: Red, painful skin that may peel after a few days.
-
Cause: Overexposure to ultraviolet (UV) rays from the sun.
-
Treatment:
-
Cool compresses and aloe vera to soothe the skin.
-
Hydration and moisturizers to aid healing.
-
Prevent future burns by applying broad-spectrum sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher.
-
🧴 General Skincare Tips for Redness-Prone Skin
-
Gentle Cleansing: Use mild, fragrance-free cleansers to avoid irritation.
-
Moisturizing: Apply non-comedogenic moisturizers to maintain skin barrier function.
-
Sun Protection: Daily application of sunscreen to prevent UV-induced damage.
-
Avoid Triggers: Identify and steer clear of personal triggers such as certain foods, extreme temperatures, or stress.
-
Consult Professionals: Seek advice from dermatologists for persistent or severe cases.
📌 When to See a Dermatologist
-
Red spots persist beyond a few weeks.
-
Symptoms worsen or spread.
-
Over-the-counter treatments are ineffective.
-
Signs of infection, such as pus, increased pain, or fever, develop.
Note: Accurate diagnosis is crucial, as treatments vary depending on the underlying cause. For instance, while topical steroids may alleviate contact dermatitis, they can exacerbate rosacea. Therefore, professional evaluation ensures appropriate and effective treatment.
If you need further information on specific treatments or product recommendations, feel free to ask!
-