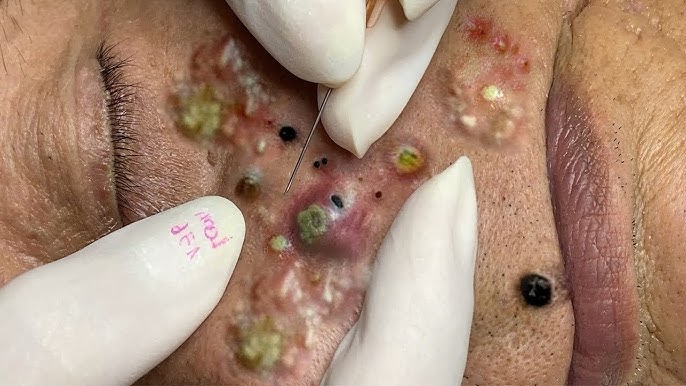
Most blackheads are caused by clogged hair follicles. The primary factors contributing to their formation include:
-
Excess Sebum (Oil) Production – When the skin produces too much oil, it can mix with dead skin cells and clog pores.
-
Dead Skin Cell Buildup – If dead skin cells aren’t shed properly, they accumulate and block pores.
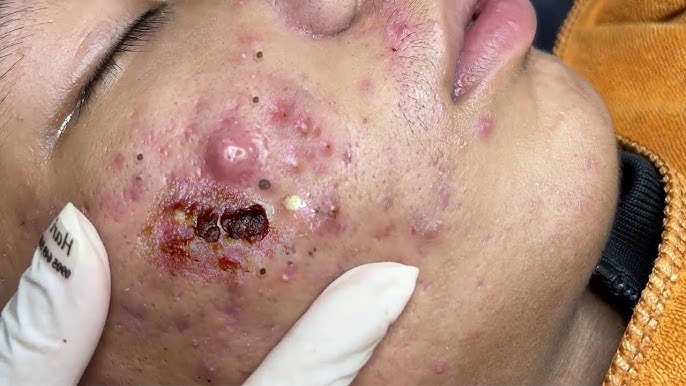
-
Hormonal Changes – Puberty, menstruation, pregnancy, and hormonal conditions (like PCOS) can increase oil production.
-
Certain Skincare or Makeup Products – Using comedogenic (pore-clogging) products can contribute to blackheads.
-
Sweat and Humidity – Excessive sweating, especially if not cleaned off properly, can contribute to clogged pores.
-
Poor Hygiene or Skincare Routine – Not cleansing the skin regularly or exfoliating can lead to buildup in pores.
-
Diet – Some studies suggest that high dairy or high glycemic-index foods may contribute to acne, including blackheads.
-
Smoking and Pollution – Environmental factors like smoke and pollution can mix with oil on the skin, leading to clogged pores.
-
Genetics – If your parents had oily skin or were prone to acne, you may be genetically predisposed to blackheads.
-
Overwashing or Harsh Skincare – Stripping the skin of its natural oils with excessive washing or strong cleansers can cause the skin to overproduce oil, leading to more clogged pores.
-
Not Removing Makeup Properly – Sleeping with makeup on or not cleansing thoroughly can lead to residue buildup that clogs pores.
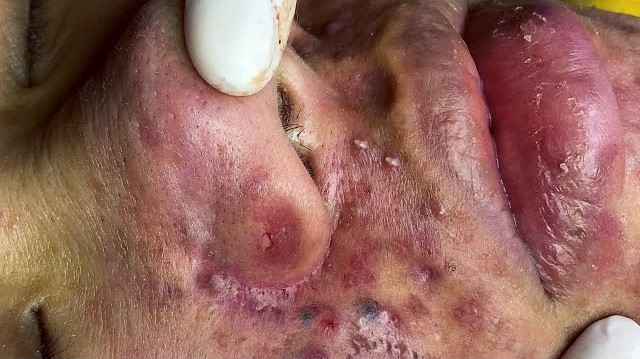
-
Using Heavy or Oily Hair Products – Pomades, gels, or conditioners with heavy oils can transfer onto the face, leading to blackheads, especially around the hairline.
-
Tight Clothing or Headwear – Items like hats, headbands, and helmets can trap oil, sweat, and bacteria against the skin, leading to blackheads, especially on the forehead.
-
Touching Your Face Too Much – Hands carry bacteria, dirt, and oils that can contribute to clogged pores when frequently touching the face.
-
Stress and Lack of Sleep – While not a direct cause, stress and poor sleep can disrupt hormones, leading to increased oil production and more breakouts, including blackheads.
-
Dehydration – When the skin is dehydrated, it can produce more oil to compensate, potentially leading to clogged pores.
-
Certain Medications – Drugs that affect hormones (such as steroids, lithium, or birth control pills) can contribute to excess oil production and blackheads.
-
Sun Exposure Without Protection – UV rays can thicken the skin over time, trapping debris in pores and making blackheads more common.
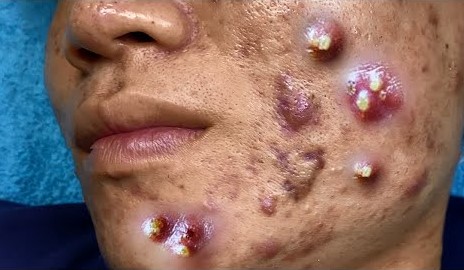
Getting rid of blackheads requires a combination of proper skincare, exfoliation, and lifestyle changes. Here are the best ways to remove and prevent blackheads:
1. Cleanse Properly
- Use a gentle cleanser with ingredients like salicylic acid to dissolve oil and unclog pores.
- Wash your face twice daily and after sweating.
- Avoid harsh soaps that strip the skin, as this can increase oil production.
2. Exfoliate Regularly
- Use a chemical exfoliant with salicylic acid, glycolic acid, or lactic acid to remove dead skin cells.
- Try a BHA (beta hydroxy acid) exfoliant 2-3 times a week to deeply clean pores.
- Avoid scrubs with large, rough particles (like walnut shells) that can irritate the skin.
3. Use Retinoids
- Retinol or prescription retinoids (like tretinoin or adapalene) help unclog pores and prevent blackheads.
- Start slowly (2-3 times a week) to avoid irritation.
- Always use sunscreen with retinoids, as they make skin more sensitive to the sun.
4. Apply Clay or Charcoal Masks
- Clay masks (like bentonite or kaolin) absorb excess oil and pull out impurities.
- Charcoal masks help draw out dirt and toxins from pores.
- Use these masks 1-2 times per week for best results.
5. Try Pore Strips (Occasionally)
- Pore strips can temporarily remove blackheads, but they don’t prevent them.
- Use them sparingly, as overuse can irritate the skin.
6. Use Non-Comedogenic Products
- Choose skincare and makeup labeled “non-comedogenic” to prevent clogging pores.
- Avoid heavy, greasy lotions and oils that can contribute to blackheads.
7. Don’t Pick or Squeeze
- Squeezing blackheads can push bacteria deeper, leading to inflammation and breakouts.
- If extraction is necessary, see a dermatologist or esthetician for a safe procedure.
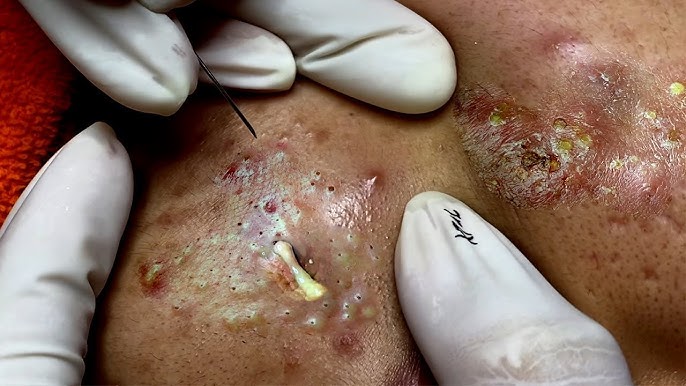
8. Keep Pillowcases & Towels Clean
- Change pillowcases at least twice a week to prevent oil and bacteria buildup.
- Use clean towels and avoid touching your face throughout the day.
9. Moisturize (Even for Oily Skin!)
- Use a lightweight, oil-free moisturizer to keep skin balanced.
- Skipping moisturizer can cause the skin to produce more oil, worsening blackheads.
10. Consider Professional Treatments
- Chemical peels (with AHAs, BHAs, or enzymes) help exfoliate deeper layers of skin.
- Microdermabrasion can help remove dead skin cells and unclog pores.
- Extractions by a professional are safer than DIY squeezing.