Large Cyst Squirts and Oozes from Patient’s Neck
Please scroll down to watch the video.👇👇
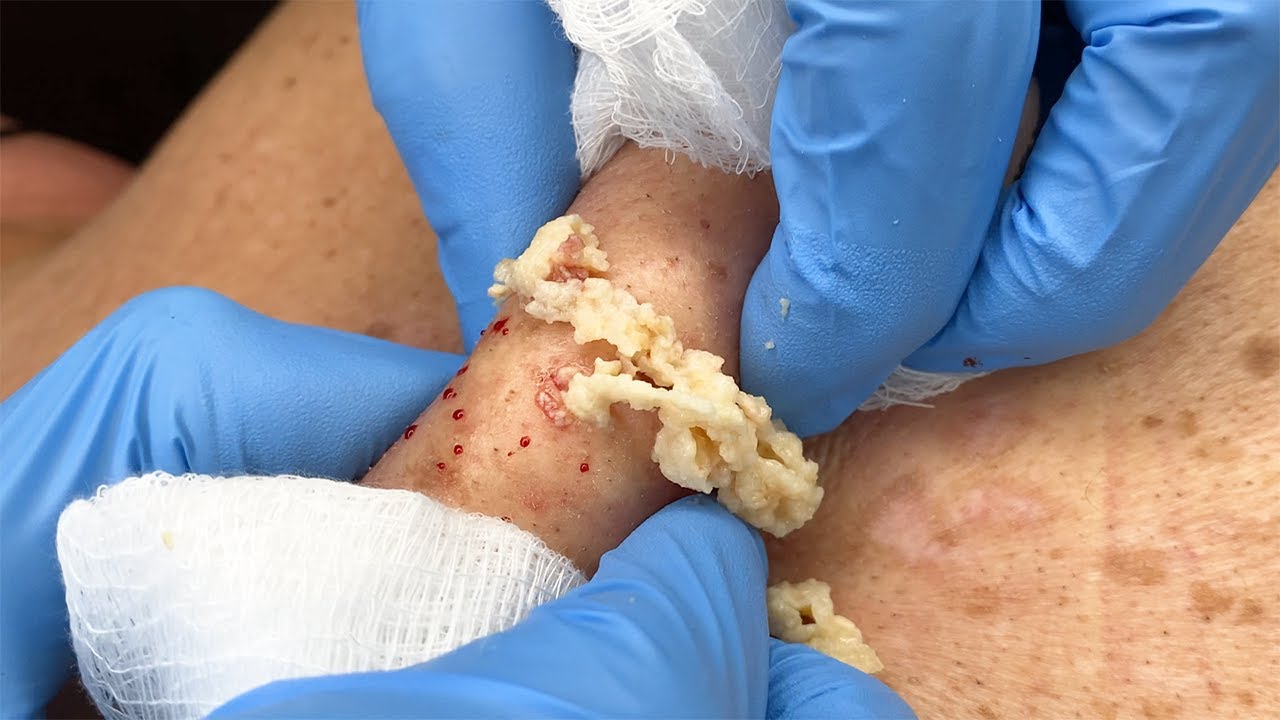
Large cysts that squirt or ooze when drained are usually due to a sebaceous cyst or epidermoid cyst—benign lumps under the skin filled with keratin or sebum. When they become infected, inflamed, or rupture, they can release a thick, often foul-smelling discharge. Here’s how this is generally handled medically (do not try to pop one yourself):
🧪 What Is Happening Medically?
-
Sebaceous/Epidermoid Cysts form when the opening of a sebaceous gland is blocked.
-
The inside fills with a cheesy, yellow-white substance made of dead skin cells and oils.
-
If pressure builds or it gets infected, it can squirt or ooze upon rupture or drainage.
⚠️ What to Do If You Have One
1. Do Not Squeeze It Yourself
-
Squeezing can push the contents deeper and worsen inflammation or infection.
-
You might cause abscess formation or scarring.
2. Warm Compresses
-
Apply a warm compress for 10–15 minutes several times a day to promote drainage if it’s small.
-
This may soften the contents and reduce discomfort.
3. Medical Drainage (Performed by a Doctor)
A healthcare provider will:
-
Clean the area with antiseptic.
-
Use local anesthesia.
-
Make a small incision to release the contents.
-
Gently express the contents using sterile tools.
-
In some cases, pack the wound to allow continuous drainage.
📌 Sometimes, oral antibiotics are needed if it’s infected.
🔄 Definitive Treatment
-
Surgical excision is required to remove the entire cyst wall and prevent recurrence.
-
This is a minor outpatient procedure done under local anesthesia.
📽️ Why Does It Squirt?
When under pressure, the cyst contents are forcefully expelled, sometimes in dramatic fashion, like in popular pimple-popping videos.
🎥 You may have seen videos from dermatologists like Dr. Sandra Lee (Dr. Pimple Popper). These procedures are done under sterile conditions and are not safe to attempt at home.
📚 References:
-
Mayo Clinic:
-
Cleveland Clinic: Epidermoid cyst
-
American Academy of Dermatology: Cyst removal
When a large cyst on the neck releases fluid—either by oozing or forceful expulsion—it is typically due to an epidermoid cyst (commonly referred to as a sebaceous cyst). These cysts are benign, slow-growing lumps beneath the skin, filled with keratin—a protein found in skin cells. While usually harmless, they can become inflamed or infected, leading to discomfort and noticeable discharge.
🧬 Understanding Epidermoid Cysts
-
Composition: Filled with keratin, a thick, yellowish substance.
-
Common Locations: Face, neck, scalp, and trunk.
-
Symptoms: Often painless unless inflamed; may have a visible central opening (punctum).
-
Causes: Can result from blocked hair follicles, skin trauma, or developmental defects.
🩺 Medical Evaluation
If you notice a lump on your neck that changes in size, becomes painful, or starts to discharge, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional. They will assess the cyst to determine the appropriate treatment, which may include monitoring, drainage, or removal.
⚠️ Important Considerations
-
Avoid Self-Treatment: Do not attempt to squeeze or drain the cyst yourself, as this can lead to infection or scarring.
-
Monitor for Changes: Keep an eye on the cyst for signs of infection, such as increased redness, warmth, or pus.
-
Seek Prompt Medical Attention: If the cyst becomes painful, rapidly enlarges, or shows signs of infection, consult a healthcare provider promptly.
-