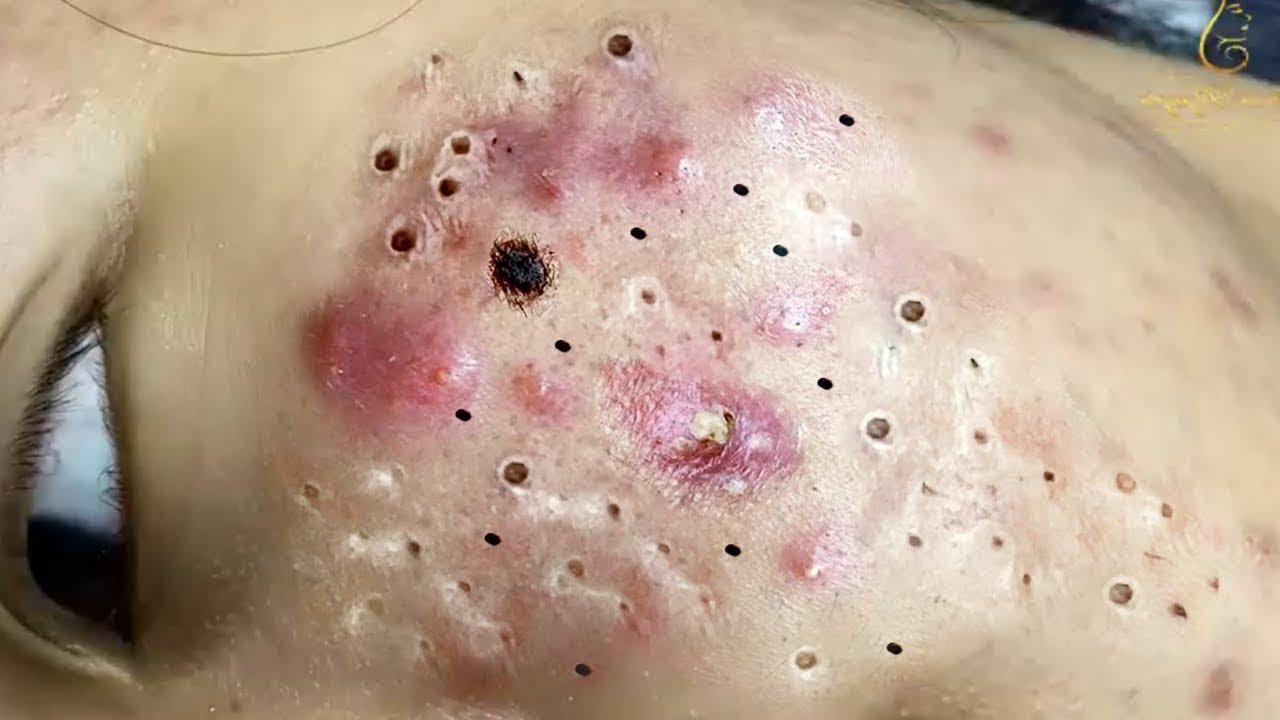
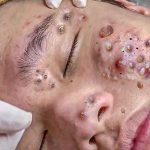
Get rid of acne scars
Please scroll down to watch the video.👇👇
Getting rid of acne scars involves a mix of skincare, medical treatments, and patience. The best approach depends on the type and severity of the scars (e.g., dark spots, raised scars, or indented scars like ice-pick or boxcar scars). Here are effective options:
🔹 At-Home Treatments (best for mild discoloration and newer scars)
-
Sunscreen (SPF 30 or higher) – Prevents dark scars from getting darker.
-
Retinoids (Retinol or Tretinoin) – Promotes cell turnover and collagen production.
-
Vitamin C Serum – Helps lighten dark spots and even skin tone.
-
Niacinamide – Reduces inflammation and hyperpigmentation.
-
Exfoliation (AHA/BHA) – Removes dead skin cells and smoothens texture.
🔹 Professional Treatments (for deeper or stubborn scars)
-
Chemical Peels – Removes the top layer of skin to reduce pigmentation and texture.
-
Microneedling – Stimulates collagen to improve indented scars.
-
Laser Therapy – Resurfaces the skin and reduces discoloration or texture.
-
Dermal Fillers – Temporarily fills in depressed scars.
-
Subcision – A minor surgical technique to release scar tissue under indented scars.
-
Punch Excision or Grafting – Used for deep, ice-pick scars.
🔹 Tips:
-
Consistency is key – Even the best products need weeks or months to work.
-
Avoid picking or squeezing – It worsens scarring.
-
Consult a dermatologist – Especially for persistent or severe scars.
Would you like product recommendations or guidance based on your skin type or scar type?
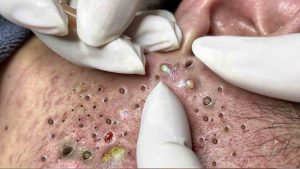
Treating acne scars effectively requires a tailored approach based on the scar type, skin tone, and severity. Here’s a detailed guide with evidence-based options:
🔹 Topical Treatments for Hyperpigmentation and Mild Scars
These are suitable for dark spots (post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation) and superficial scars:
-
Retinoids (e.g., Tretinoin, Adapalene): Stimulate collagen production and accelerate skin cell turnover, improving texture and fading discoloration.
-
Vitamin C: An antioxidant that inhibits melanin production, helping to lighten dark spots and even out skin tone.
-
Niacinamide: Reduces inflammation and can help fade hyperpigmented spots.
-
Hydroquinone: A skin-lightening agent that decreases melanin production. While effective, it should be used under medical supervision due to potential side effects like ochronosis with prolonged use.
-
Sunscreen (SPF 30 or higher): Essential to prevent further darkening of scars and protect healing skin.
🔹 Professional Procedures for Moderate to Severe Scarring
For deeper or more persistent scars, dermatological treatments offer more significant results:
-
Chemical Peels: Utilize acids like glycolic or trichloroacetic acid (TCA) to exfoliate the skin, improving texture and reducing discoloration. Medium to deep peels can address more pronounced scars but may carry higher risks of side effects.
-
Microneedling (Collagen Induction Therapy): Involves using fine needles to create micro-injuries, stimulating collagen production and improving the appearance of atrophic scars. Combining microneedling with platelet-rich plasma (PRP) may enhance results, though more research is needed.
-
Laser Therapy:
-
Ablative Lasers (e.g., CO₂, Er:YAG): Remove layers of skin to reduce deeper scars but require longer recovery times.
-
Non-Ablative Lasers (e.g., Nd:YAG, Fraxel): Stimulate collagen without removing skin layers, suitable for less severe scarring with minimal downtime.
-
-
Subcision: A minor surgical procedure that releases fibrous bands beneath depressed scars, allowing the skin to rise and appear smoother.
-
Dermal Fillers: Injectable substances like hyaluronic acid can temporarily elevate depressed scars, providing immediate improvement.
-
Dermabrasion: A mechanical exfoliation technique that removes the top skin layers, effective for certain scar types but less commonly used due to the advent of laser technologies.
🔹 Natural Remedies and Over-the-Counter Options
While not as potent as medical treatments, some natural and OTC remedies may offer mild improvements:
-
Aloe Vera, Honey, Coconut Oil: Known for their soothing and moisturizing properties, they may aid in minor scar healing.
-
Over-the-Counter Creams: Products containing ingredients like glycolic acid, retinoids, or vitamin C can help improve skin texture and tone over time.
🔹 Preventive Measures
-
Avoid Picking or Squeezing Acne: This can exacerbate inflammation and increase the risk of scarring.
-
Early Treatment: Addressing acne promptly can prevent the formation of scars.
-
Sun Protection: Regular use of sunscreen helps prevent hyperpigmentation and supports the healing process.