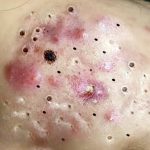
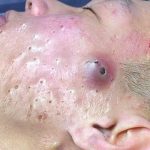
Acne scars treatment .
Please scroll down to watch the video.👇👇
Treating acne scars involves a combination of skincare, professional treatments, and lifestyle habits. The best method depends on the type and severity of the scars (e.g., atrophic, hypertrophic, or dark spots). Here’s a breakdown of effective options:
🧴 Topical Treatments (for mild scarring & discoloration):
-
Retinoids (e.g., tretinoin, adapalene):
-
Stimulate collagen and cell turnover.
-
Help fade dark marks and smooth skin texture.
-
-
Vitamin C serum:
-
Brightens skin and reduces pigmentation.
-
-
Niacinamide:
-
Reduces redness, inflammation, and pigmentation.
-
-
AHAs/BHAs (e.g., glycolic acid, salicylic acid):
-
Exfoliate skin, improve texture, and unclog pores.
-
🧑⚕️ Professional Dermatological Treatments:
-
Microneedling:
-
Tiny needles stimulate collagen to improve atrophic (depressed) scars.
-
Often combined with PRP (platelet-rich plasma) for better results.
-
-
Chemical Peels:
-
Stronger than over-the-counter exfoliants.
-
Remove damaged top layers to promote new skin growth.
-
-
Laser Treatments (e.g., fractional CO2, Er:YAG):
-
Resurfaces the skin and stimulates collagen.
-
Best for deeper scars.
-
-
Dermal Fillers:
-
Temporarily lift depressed scars (like boxcar or rolling scars).
-
-
Subcision:
-
Minor surgical procedure to release fibrous bands pulling the skin down.
-
🧼 Daily Habits for Best Results:
-
Use sunscreen daily (SPF 30+). UV exposure makes scars worse.
-
Avoid picking or squeezing acne.
-
Maintain a consistent skincare routine with non-comedogenic products.
-
Treat active acne early to prevent new scars.
Treating acne scars effectively requires a tailored approach based on the scar type, skin tone, and individual preferences. Here’s a detailed overview of evidence-based treatments, supported by clinical studies and expert recommendations:
🧬 Types of Acne Scars
-
Atrophic Scars: Depressed scars resulting from collagen loss, including:
-
Ice pick: Narrow and deep.
-
Boxcar: Broad with sharp edges.
-
Rolling: Wavy with sloped edges.
-
-
Hypertrophic/Keloid Scars: Raised scars due to excess collagen production.
-
Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation (PIH): Dark spots remaining after acne heals.
🧴 Topical Treatments
While topical treatments are less effective for deep scars, they can help with discoloration and skin texture:
-
Retinoids (e.g., tretinoin, adapalene): Promote collagen production and cell turnover.
-
Vitamin C: Brightens skin and reduces pigmentation.
-
Niacinamide: Reduces inflammation and improves skin elasticity.
-
Alpha Hydroxy Acids (AHAs) & Beta Hydroxy Acids (BHAs): Exfoliate the skin, improving texture and tone.
🧑⚕️ Professional Treatments
1. Microneedling
Involves creating micro-injuries to stimulate collagen production.
-
Efficacy: Studies show significant improvement in atrophic scars, with minimal side effects.
-
Combination Therapies: Enhanced results when combined with platelet-rich plasma (PRP).
2. Laser Treatments
Use concentrated light to resurface the skin and stimulate collagen.
-
Fractional CO₂ Lasers: Effective for deep atrophic scars.
-
Non-Ablative Lasers: Suitable for patients seeking less downtime.
3. Chemical Peels
Apply chemical solutions to exfoliate and improve skin texture.
-
Mild Peels: Use glycolic or salicylic acid for superficial scars.
-
Medium to Deep Peels: Employ trichloroacetic acid (TCA) for more pronounced scars.
4. Subcision
A minor surgical procedure that releases fibrous bands beneath scars, allowing the skin to rise.
-
Best For: Rolling scars.
5. Dermal Fillers
Injectable substances that fill in depressed scars.
-
Options: Hyaluronic acid, poly-L-lactic acid, and others.
🌞 Daily Skincare and Prevention
-
Sun Protection: Use broad-spectrum sunscreen (SPF 30+) to prevent hyperpigmentation.
-
Avoid Picking: Reduces the risk of scarring.
-
Consistent Skincare Routine: Incorporate non-comedogenic products with ingredients like retinoids and vitamin C.
-