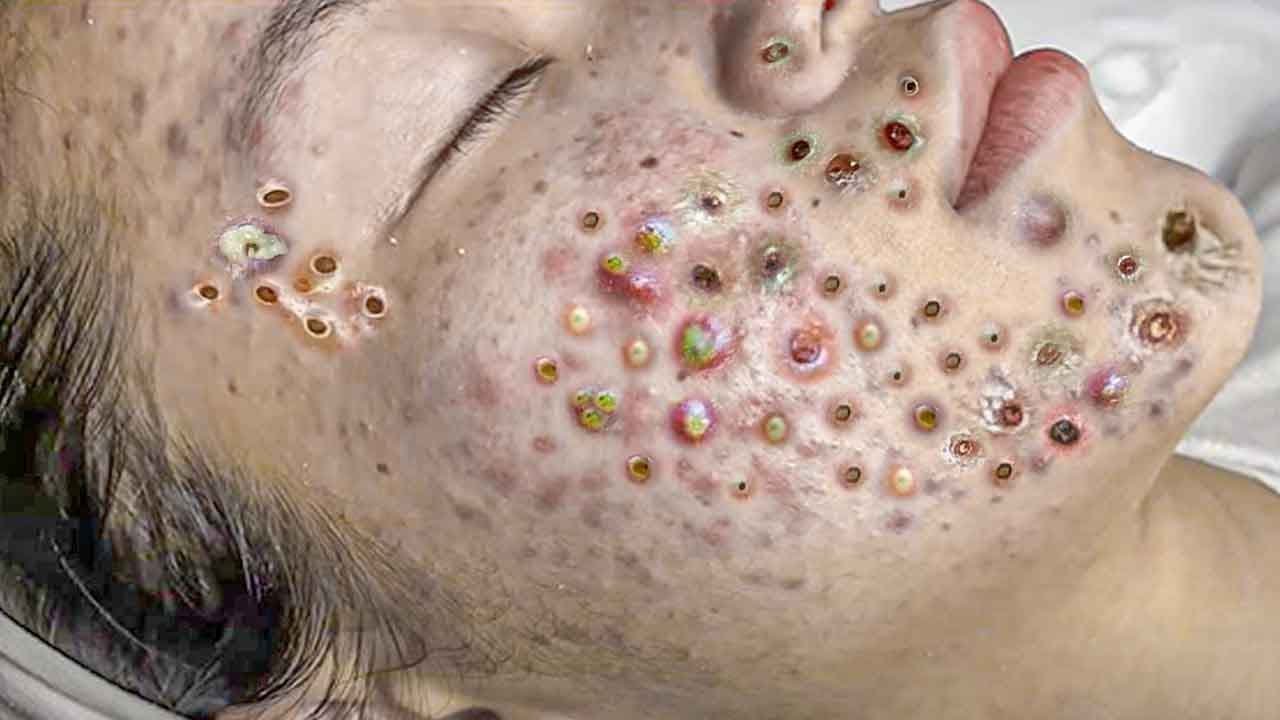
Acne extractions on severe inflammatory acne. Multiple blackheads and whiteheads.
Please scroll down to watch the video.👇👇
Acne extraction on severe inflammatory acne (with multiple blackheads and whiteheads) must be done with caution, ideally by a dermatologist or trained professional. Attempting it improperly can worsen inflammation, cause scarring, or spread bacteria. However, here’s a detailed overview of the professional method used for extractions, which should not be done at home for severe cases:
⚠️ WARNING:
For severe inflammatory acne (especially with cysts, nodules, or large pustules), do not attempt extraction yourself. Seek a dermatologist or licensed esthetician. Home extraction increases the risk of:
-
Permanent scarring
-
Infection
-
Worsening of acne
✅ Professional Extraction Process:
1. Preparation
-
Client skin assessment: Confirm type of acne (non-inflammatory vs inflammatory, active infections, etc.)
-
Cleanse thoroughly with a gentle, non-comedogenic cleanser.
-
Apply warm steam or a warm compress for 10–15 minutes to open pores and soften sebum.
2. Disinfection
-
Wear gloves.
-
Use sterilized tools (like comedone extractors) and antiseptic wipes to prep the skin.
-
Tools: comedone extractor loop, lancet (for whiteheads only), cotton swabs, sterile gauze.
3. Extraction Techniques
🔹 Blackheads (Open Comedones)
-
Gently press the loop of the comedone extractor around the blackhead.
-
Apply even pressure downward and then pull slightly to the side.
-
Wipe extracted material with sterile gauze.
🔹 Whiteheads (Closed Comedones)
-
Use a sterile lancet to gently nick the whitehead surface.
-
Then, use cotton swabs or a comedone extractor to press gently and remove the contents.
🔹 Inflamed Papules, Pustules, or Cysts
-
DO NOT EXTRACT if inflamed or painful.
-
These should be treated with:
-
Topical/oral antibiotics
-
Cortisone injections (in-office)
-
Benzoyl peroxide, retinoids, or salicylic acid
-
4. Aftercare
-
Apply antiseptic or anti-inflammatory toner (e.g., witch hazel, chamomile).
-
Use a cool compress to reduce redness and swelling.
-
Apply a healing serum with ingredients like niacinamide, centella asiatica, or hyaluronic acid.
-
Advise no makeup or touching the face for at least 24 hours.
Alternatives to Extraction for Severe Cases
If the acne is widespread or inflamed, consider:
-
Chemical peels (salicylic or glycolic acid)
-
HydraFacial with extraction
-
Oral medications (antibiotics, hormonal treatments)
-
Isotretinoin (for cystic acne, prescribed only by a doctor)
Performing acne extractions on severe inflammatory acne—characterized by multiple blackheads, whiteheads, and inflamed lesions—requires meticulous care and should ideally be conducted by a licensed dermatologist or trained esthetician. Improper extraction can exacerbate inflammation, lead to scarring, or cause infections. Below is a detailed, evidence-based protocol for professional acne extraction, along with references for further reading.
🔬 Professional Acne Extraction Protocol
1. Assessment and Preparation
-
Evaluate the Acne Type: Confirm that the lesions are suitable for extraction. Non-inflamed comedones (blackheads and whiteheads) are appropriate, whereas inflamed papules, pustules, nodules, or cysts should not be extracted due to the risk of scarring and infection.
-
Cleanse the Skin: Use a gentle, non-comedogenic cleanser to remove surface impurities.
-
Apply Warmth: Use warm steam or a warm compress for 10–15 minutes to soften the skin and open pores, facilitating easier extraction.
-
Desincrustation: Apply a desincrustation solution or mask to further soften keratin plugs within the pores. This step enhances the efficacy of extractions and minimizes trauma to surrounding tissues.
2. Sterilization and Hygiene
-
Hand Hygiene: Thoroughly wash hands and wear disposable gloves to maintain a sterile environment.
-
Sterilize Tools: Ensure all extraction instruments, such as comedone extractors and lancets, are properly sterilized before use to prevent bacterial contamination.
3. Extraction Techniques
a. Blackheads (Open Comedones)
-
Technique: Place the loop of a comedone extractor over the blackhead and apply gentle, even pressure to expel the contents.
-
Angle and Pressure: Hold the extractor parallel to the skin and apply light pressure in the direction of the pore to minimize skin trauma.
b. Whiteheads (Closed Comedones)
-
Incision: If necessary, use a sterile lancet to make a small opening in the whitehead.
-
Extraction: Gently press around the lesion with the comedone extractor or gloved fingers wrapped in sterile gauze to remove the contents.
c. Inflamed Lesions (Papules, Pustules, Nodules, Cysts)
-
Avoid Extraction: Do not attempt to extract inflamed lesions, as this can worsen inflammation and increase the risk of scarring.
-
Alternative Treatments: Consider medical therapies such as topical or oral antibiotics, corticosteroid injections, or other dermatologist-recommended treatments.
4. Post-Extraction Care
-
Antiseptic Application: Apply an antiseptic solution containing salicylic acid or tea tree oil to the treated areas to prevent infection and soothe the skin.
-
Cool Compress: Use a cool compress to reduce redness and swelling.
-
Hydration: Apply a non-comedogenic moisturizer to maintain skin hydration.
-
Sun Protection: Advise the use of sunscreen to protect the skin, as it may be more sensitive post-extraction.
⚠️ Important Considerations
-
Professional Training: Extractions should only be performed by trained professionals to minimize risks.
-
Avoid Home Extractions: Self-extraction can lead to complications such as scarring, infection, and worsening of acne.
-
Regular Treatments: For ongoing acne management, schedule regular professional treatments as recommended by a dermatologist.
📚 References
-