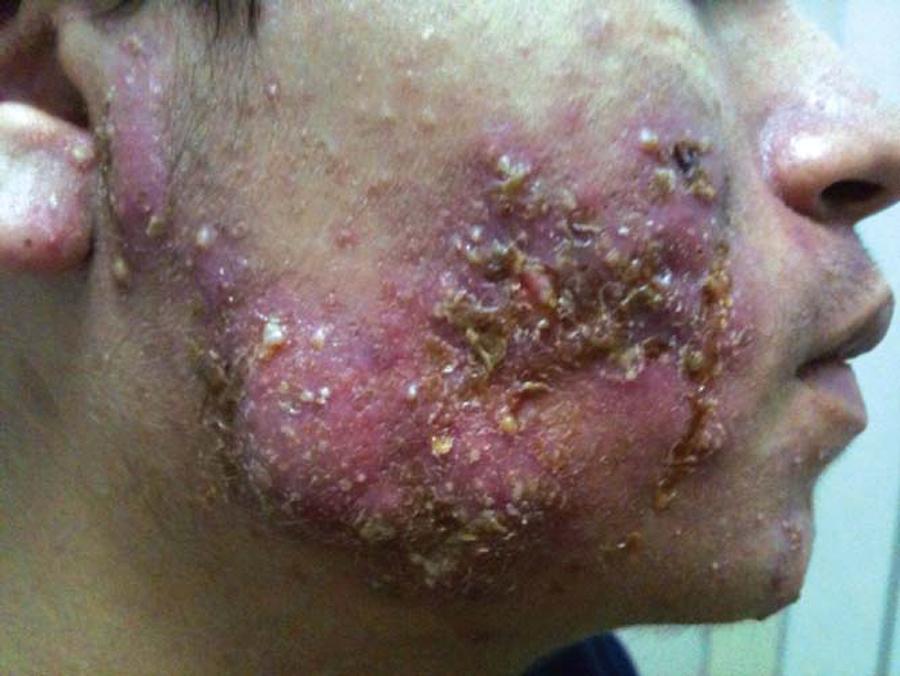
Taking care of your face to prevent acne involves a combination of proper cleansing, hydration, diet, and lifestyle habits. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
1. Proper Cleansing
- Wash your face twice daily (morning & night) with a gentle cleanser suited for your skin type.
- Use lukewarm water (hot water can strip moisture, cold water won’t remove oil properly).
- If you wear makeup, remove it completely with micellar water or an oil-free makeup remover before washing your face.
- Don’t over-wash—excess washing can lead to dryness and irritation, triggering more oil production.
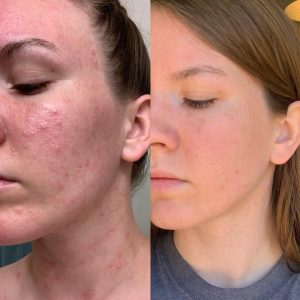
2. Hydration & Moisturizing
- Use a lightweight, non-comedogenic moisturizer to keep skin hydrated.
- Avoid heavy, oily products that can clog pores.
- Drink plenty of water to keep skin healthy and flush out toxins.
3. Exfoliation & Treatment
- Exfoliate 1–2 times a week using a gentle exfoliant (avoid harsh scrubs).
- Use salicylic acid or glycolic acid to keep pores clear.
- If you have occasional breakouts, apply benzoyl peroxide or tea tree oil as a spot treatment.
4. Sun Protection
- Use a broad-spectrum sunscreen (SPF 30+) every day, even in winter.
- Choose a sunscreen that is oil-free and non-comedogenic.
5. Diet & Lifestyle
- Eat a balanced diet rich in vegetables, fruits, and healthy fats.
- Avoid excessive sugar, dairy, and processed foods, which may trigger acne in some people.
- Manage stress with exercise, meditation, or good sleep—stress can increase oil production.
- Change your pillowcases weekly and avoid touching your face to prevent bacteria buildup.
How to Take Care of Your Face Without Acne
Achieving and maintaining clear skin requires a combination of proper skincare, a healthy lifestyle, and consistency. Below is a detailed guide on how to prevent acne and keep your face healthy.
1. Cleansing: The Foundation of Clear Skin
Cleansing helps remove dirt, oil, and bacteria that can clog pores and cause acne.
How to Cleanse Properly
✅ Wash your face twice daily – once in the morning and once at night.
✅ Use a gentle, sulfate-free cleanser that suits your skin type (oily, dry, combination, or sensitive).
✅ Avoid harsh soaps that strip natural oils, which can lead to more oil production.
✅ Double cleanse at night if you wear makeup or sunscreen. Start with an oil-based cleanser, followed by a gentle water-based cleanser.
✅ Use lukewarm water – hot water can dry out the skin, and cold water won’t remove oil effectively.
✅ Pat your face dry with a clean towel (don’t rub).
Best Ingredients in a Cleanser for Acne-Prone Skin:
- Salicylic Acid – unclogs pores and prevents breakouts.
- Benzoyl Peroxide – kills acne-causing bacteria.
- Tea Tree Oil – has natural antibacterial properties.
- Niacinamide – reduces inflammation and oil production.
2. Hydration & Moisturizing: Essential for Balanced Skin
Even oily and acne-prone skin needs hydration to maintain balance and prevent excessive oil production.
How to Hydrate & Moisturize Properly
✅ Use a lightweight, non-comedogenic moisturizer to keep skin hydrated.
✅ Choose gel-based or water-based moisturizers for oily skin and cream-based for dry skin.
✅ Hyaluronic acid is great for hydration without clogging pores.
✅ Aloe vera is soothing and anti-inflammatory.
Recommended Moisturizers for Acne-Prone Skin:
- CeraVe PM Facial Moisturizing Lotion
- Neutrogena Hydro Boost Water Gel
- La Roche-Posay Effaclar Mat
3. Exfoliation: Removing Dead Skin Cells
Exfoliation helps clear clogged pores, but over-exfoliating can irritate the skin and make acne worse.
How to Exfoliate Safely
✅ Use a chemical exfoliant (2–3 times a week) like:
- Salicylic Acid (BHA) – penetrates deep into pores and dissolves oil.
- Glycolic Acid (AHA) – removes dead skin cells and brightens skin.
✅ Avoid physical scrubs (like walnut or apricot scrubs) as they can cause micro-tears.
Best Exfoliators for Acne-Prone Skin:
- Paula’s Choice 2% BHA Liquid Exfoliant
- The Ordinary Glycolic Acid 7% Toner
4. Acne Treatments: Targeting Breakouts
If you still get pimples, spot treatments can help reduce them quickly.
Best Ingredients for Acne Treatment
✅ Benzoyl Peroxide (2.5%–5%) – kills acne bacteria and reduces inflammation.
✅ Tea Tree Oil – natural antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties.
✅ Retinoids (Adapalene, Tretinoin) – unclog pores and prevent new acne.
✅ Clay Masks (Kaolin or Bentonite) – absorb excess oil and detoxify the skin.
5. Sun Protection: Preventing Dark Spots & Irritation
Many acne treatments (especially acids and retinoids) make your skin more sensitive to sunlight.
How to Choose the Right Sunscreen
✅ Use an oil-free, non-comedogenic sunscreen with SPF 30+.
✅ Choose lightweight formulas like gels or fluids for acne-prone skin.
✅ Avoid sunscreens with fragrance, alcohol, or heavy oils.
Best Sunscreens for Acne-Prone Skin:
- EltaMD UV Clear SPF 46
- La Roche-Posay Anthelios Melt-In Milk Sunscreen SPF 60
- Neutrogena Clear Face Sunscreen SPF 50
6. Lifestyle Changes for Acne-Free Skin
Diet & Nutrition
✅ Eat more:
- Fruits & vegetables (rich in antioxidants & vitamins).
- Omega-3 fatty acids (found in salmon, flaxseeds, walnuts).
- Zinc-rich foods (pumpkin seeds, chickpeas, cashews) to reduce inflammation.
✅ Avoid excessive: - Dairy (milk, cheese) – can trigger acne in some people.
- Sugar & processed foods – cause insulin spikes, increasing oil production.
- Greasy, fried foods – can worsen inflammation.
Good Habits for Clear Skin
✅ Change pillowcases weekly – bacteria and oil build up can clog pores.
✅ Clean your phone screen – touching your face with a dirty phone transfers bacteria.
✅ Avoid touching your face – prevents bacteria from spreading to your skin.
✅ Reduce stress – cortisol (stress hormone) triggers oil production. Try exercise, meditation, or deep breathing.
✅ Get 7–9 hours of sleep – lack of sleep increases stress hormones, leading to breakouts.
Final Tips for Clear Skin
✔ Stick to a simple, consistent routine – switching products too often can irritate your skin.
✔ Be patient – skincare takes time; results usually show after 4–6 weeks.
✔ If acne persists, consult a dermatologist for prescription treatments like retinoids or antibiotics.